Explain the Similarities and Differences Between Monomers and Polymers
In doing so monomers release water molecules as byproducts. A large number of monomers combine with the loss of simple molecules water ammonia HCl alcohol to form a polymer having molecular formula of the repeating unit.

Examples Of Linear And Branched Polymers The Structural Formulas Of Download Scientific Diagram
Both DNA and RNA consists of sugar nitrogenous bases and a phosphate backbone.

. For example ethylene glycol reacts with terephathalate to form poly ethylene terephathalate polymer. Polymers are made from monomers. Polymers are formed essentially.
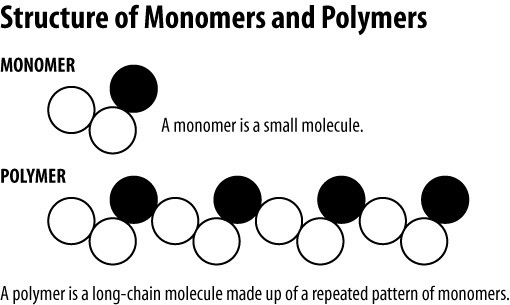
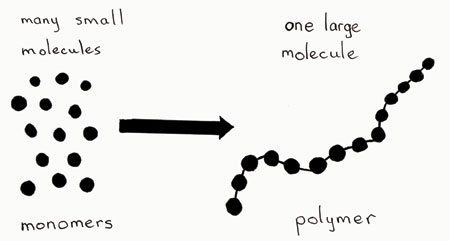
The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. A polymer is a macromolecular material having a large number of repeating units linked to each other via covalent chemical bonds. A polymer is a macroscopic material built from a large number of repeating single units bound together.
The key difference between polymer and monomer is that a polymer is a collection of a large number of molecules whereas monomer is a single molecule. The double bonds are broken and linked with. Glucose hence they are very similar polymers.
Polymers are complex molecules with very high molecular weight. Remember that the brackets denote one repeat unit in a polymer a long chain of repeat units. -Fatty acids are the monomers for lipids for example and regardless of how they are bonded as a saturated or unsaturated fat for example they will form lipids.
A monomer is more mobile than a polymer. 1 Answer Samantha C. By-products such as ammonia water and HCl are produced.
These repeating units represent the monomers that were used to make the polymer. Compare actin and tubulin. Compare your answer to a comparison of the in.
Difference Between Monomer and Polymer Definition. Monomers bond together to form polymers during a chemical reaction called polymerization as the molecules link together by sharing electrons. A monomer is a single atom small molecule or molecular fragment that when bonded together with identical and similar types of monomers form a larger macromolecule known as a polymer.
Dwayne Media Owl Aug 27 2014 Monomers are smaller molecules and when bonded together make up polymers. Compare the processes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis. A monomer can have different combination units.
Polymers are complex molecules with very high molecular weight. As their monomer is the same so they also have the same glucose-based repeat units. A monomer can have different combination units.
-Nucleotides form nucleic acids eg. Monomers are the building blocks of polymers. On both molecules guanine and cytosine pair with each other are complementary.
How does a change in the subunits of a polymer lead to changes in structure or function of the macromolecule. Glycogen is an even more highly branched polysaccharide of glucose monomers that serves a function of energy storage in animals. Monomers are simple molecules with low molecular weights.
Starch serves as energy storage in plants. Macromolecules may or may not be made from monomers. For example a molecule of poly.
Furthermore monomers have a small molecular weight while the polymers have a larger molecular weight which is many times the weight of a monomer. Some polymers are soluble in organic solvents. They include the proteins polymers of amino acids nucleic acids polymers of.
Explain the relationship between monomers and polymers. Both DNA and RNA store genetic information. Both consist of many glucose monomers connected into a polymer.
Polymers are large molecular structures made of many monomers. Monomers must have either a double bond or triple bond. Polymers are macromolecules with very high molecular weights built from many repetitive units called monomers.
Different monomers add to form a polymer with same molecular formula of the repeating structural unit as that of starting monomer. Normally addition polymerization means that two monomers react with each other and no other small molecules are generaged. Cellulose is comparatively much stronger than starch.
This means they are both made of the same atomic elements however the dynamics and mechanics of. Starch and cellulose are made from the same monomer ie. A monomer in turn can consist of or is composed of one to many atoms which repeatedly makes up the structure of a polymer.
DNA and RNA are both large biological polymers. A polymer can also be explained as a macromolecule formed by chemical bonding of larger numbers of molecules being added up together now these repeating units are called monomers as mentioned earlier. Carbohydrates lipids proteins and nucleic acids.
Monomers are small molecules in the microscopic scale which cannot be compared to the macroscopic properties of polymers and they are chemically more reactive than polymers. Describe the given chemical structure of Amberlyst 15 and explain some of the similarities and differences between this and Sulfuric Acid. Remember that the brackets denote one repeat unit in a polymer a long chain of repeat units.
Addition of monomers results in. Bonding two molecules together to make a larger molecule by removing water is dehydration synthesis while adding water to split. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers.
As nucleic acids DNA and RNA share some similarities. Describe 3 or more shared features and 3 or more important differences between these. Most macromolecules are highly insoluble in water and other similar solvents.
Comparing the Biological Macromolecules Dehydration Synthesis Most macromolecules are made from single subunits or building blocks called monomers. Polymer A polymer is a chemical composed of many repeat units. Monomers are single units that act as the building blocks of polymers.
Monomers are simple molecules with low molecular. The same way that links are like a chain or bricks are like a house. Explain how the identified features contribute to similarities or differences in the in vitro behavior of the polymers actin filament AFs and microtubules MTs.
Answer 1 of 2. Hence the monomers undergo a process called polymerization to form a polymer. Meanwhile water is generated.
Polymers are made by chemical reactions that join lots of small molecules together to make long molecules. Monomers must have two similar or different functional groups. The best example is polymerization of ethylene.
Glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and muscles.

Carbon Monomers And Polymers Ck 12 Foundation

Monomer And Polymer Design A Molecular Structures Of The Different Download Scientific Diagram

Difference Between Polymer And Monomer Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Question What Is The Difference Between Monomers And Polymers Seniorcare2share

Monomers Polymers Overview Examples What Are Monomers Polymers Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
What Are The Monomers And Polymers Of Protein Socratic

Difference Between Polymer And Monomer Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Question What Is The Difference Between Monomers And Polymers Seniorcare2share

Difference Between Monomer And Polymer With Table Ask Any Difference

Molecules Of Life Introduction Reading Models Carbohydrates Lipids Ppt Video Online Download
Difference Between Polymer And Macromolecule Definition Classification General Properties And Differences
Difference Between Monomer And Polymer
Difference Between Monomer And Polymer

Difference Between Polymer And Macromolecule Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Synthesis Of Ionic Polymers By Free Radical Polymerization Using Aprotic Trimethylsilylmethyl Substituted Monomers Kaestner 2020 Journal Of Polymer Science Wiley Online Library

Monomer Vs Polymer What S The Difference Osborne Industries
What Is The Difference Between Monomers And Polymers Socratic

Question What Is The Difference Between Monomers And Polymers Seniorcare2share
Comments
Post a Comment